Critical Security Notice
Windows 8 reached End-of-Life in January 2016, and Windows 8.1 reached EOL in January 2023. Using these operating systems exposes you to unpatched security vulnerabilities. Microsoft no longer provides security updates.
Additionally, L2TP/IPSec is an older protocol with known security limitations. TorGuard strongly recommends:
- Upgrading to Windows 10 or 11 immediately
- Using OpenVPN or WireGuard for better security
- If you must use Windows 8/8.1, consider switching to a supported Linux distribution
This guide will walk you through setting up L2TP/IPSec VPN on Windows 8 and 8.1. While L2TP/IPSec provides better security than PPTP, it's still considered less secure than modern VPN protocols. We strongly recommend using OpenVPN or WireGuard instead for optimal security and performance.
Step 1: Open Network and Sharing Center
Click on "Open Network and Sharing Center" from the network icon in the taskbar, or navigate to it through Control Panel.

Step 2: Create a New Connection
Click on "Set up a new connection or network" to begin the VPN setup process.

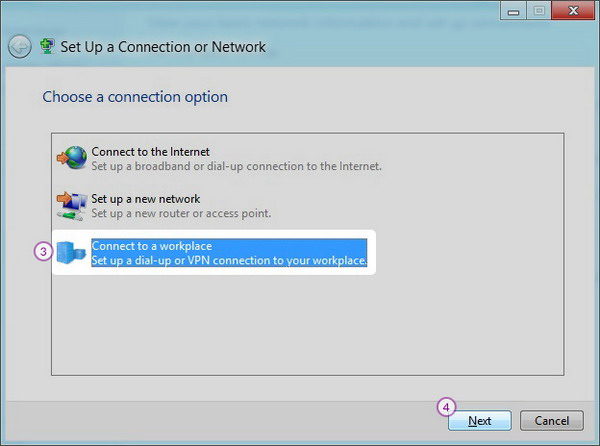
Step 3: Select Connection Type
Select "Connect to a workplace" and click "Next" to continue.
Step 4: Choose VPN Connection
Choose "Use my Internet Connection (VPN)" to create a VPN connection.

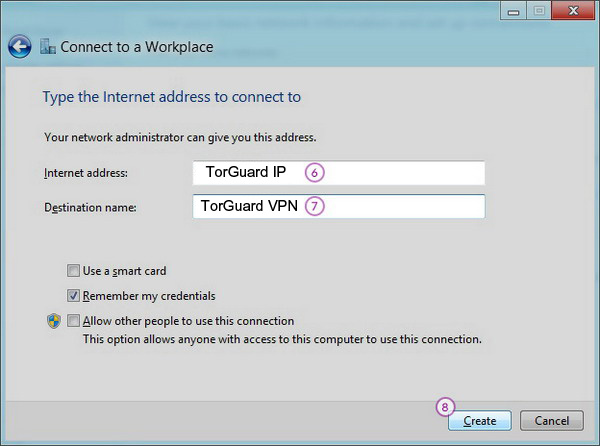
Step 5: Enter Server Details
Configure the following connection details:
- Internet Address: Enter a TorGuard VPN server IP address or hostname. You can find available servers in your TorGuard client area under "My Servers".
- Destination name: Enter "TorGuard VPN (L2TP)" or any name you prefer.
Click "Create" to save the connection.
Step 6: Access Connection Properties
Click on the network icon in the system tray (bottom-right corner).

Step 7: Open VPN Properties
Right-click on "TorGuard VPN (L2TP)" connection and choose "Properties" from the menu.

Step 8: Configure Security Settings
In the Properties window:
- Select the "Security" tab
- For "Type of VPN", select "Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec (L2TP/IPsec)"
- Click on "Advanced Settings"

Step 9: Enter Pre-shared Key
In the Advanced settings dialog:
- Select "Use preshared key for authentication"
- Enter the pre-shared key:
torguard - Click "OK" to save the settings

Step 10: Connect to VPN
Click the network icon again and click "Connect" for "TorGuard VPN (L2TP)".

Step 11: Enter Credentials
Enter your TorGuard VPN credentials:
- Username: Your TorGuard VPN username
- Password: Your TorGuard VPN password
Click "OK" to connect.

Step 12: Verify Connection
When successfully connected, you'll see "Connected" next to "TorGuard VPN (L2TP)" in the network connections.

Security Recommendations
Important Security Information
L2TP/IPSec, while more secure than PPTP, has several limitations:
- Can be blocked by some firewalls due to its use of UDP port 500 and ESP
- Potentially compromised by NSA according to Edward Snowden revelations
- Slower than modern protocols due to double encapsulation
- More complex NAT traversal compared to other protocols
Recommended Alternatives
| Protocol | Security | Speed | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | Excellent | Good | Highly Recommended |
| WireGuard | Excellent | Excellent | Highly Recommended |
| L2TP/IPSec | Moderate | Moderate | Legacy Support Only |
Troubleshooting
- Error 789: This typically indicates a firewall blocking L2TP traffic. Ensure UDP ports 500, 4500, and ESP (Protocol 50) are allowed.
- Error 809: Usually caused by incorrect pre-shared key or server not responding. Verify the pre-shared key is exactly "torguard" (lowercase).
- Slow connection speeds: L2TP/IPSec has inherent overhead. Consider switching to OpenVPN or WireGuard for better performance.
- Connection drops frequently: May be due to NAT-T issues. Try connecting from a different network or use a more modern protocol.
- Cannot access local network: Check if "Use default gateway on remote network" is enabled in the IPv4 properties of the VPN connection.
If you continue experiencing issues, please contact our support team. We strongly recommend upgrading to a supported operating system and using a more secure VPN protocol for your safety.