🔒 About L2TP/IPSec
L2TP/IPSec combines Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPSec encryption for secure VPN connections. While more secure than PPTP, it's an older protocol that modern alternatives like WireGuard and IKEv2 have largely superseded.
Protocol Security Comparison
⚠️ L2TP/IPSec (This Guide)
- Moderate security with IPSec
- Can be blocked by firewalls
- Slower than modern protocols
- Double encapsulation overhead
- Pre-shared key vulnerabilities
✅ WireGuard (Recommended)
- State-of-the-art cryptography
- Minimal attack surface
- Best performance
- Simple configuration
- Available in RouterOS 7+
✅ IKEv2/IPSec
- Modern IPSec implementation
- Better than L2TP/IPSec
- MOBIKE support
- Hardware acceleration
- Enterprise standard
Mikrotik RouterOS Requirements
Prerequisites
- RouterOS version 6.0 or higher
- IPSec package installed (default in most installations)
- Sufficient CPU for encryption (especially for AES-256)
- Administrator access to router
- TorGuard VPN account with L2TP support
IPSec Encryption Options
| Parameter | AES-128 (Faster) | AES-256 (Stronger) | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | aes-128-cbc | aes-256-cbc | AES-128 for most users |
| Hash | SHA1 | SHA1 | Limited by L2TP spec |
| DH Group | None | None | Not used with PSK |
| CPU Impact | ~10-20% | ~20-40% | Monitor router load |
Step-by-Step Configuration
1Access Mikrotik Router
Connect using one of these methods:
- WebFig: http://[router-ip] (ensure WebFig interface)
- WinBox: Download from mikrotik.com (recommended)
- SSH:
ssh admin@[router-ip]
2Configure IPSec Proposal
Navigate to: IP → IPsec → Proposals
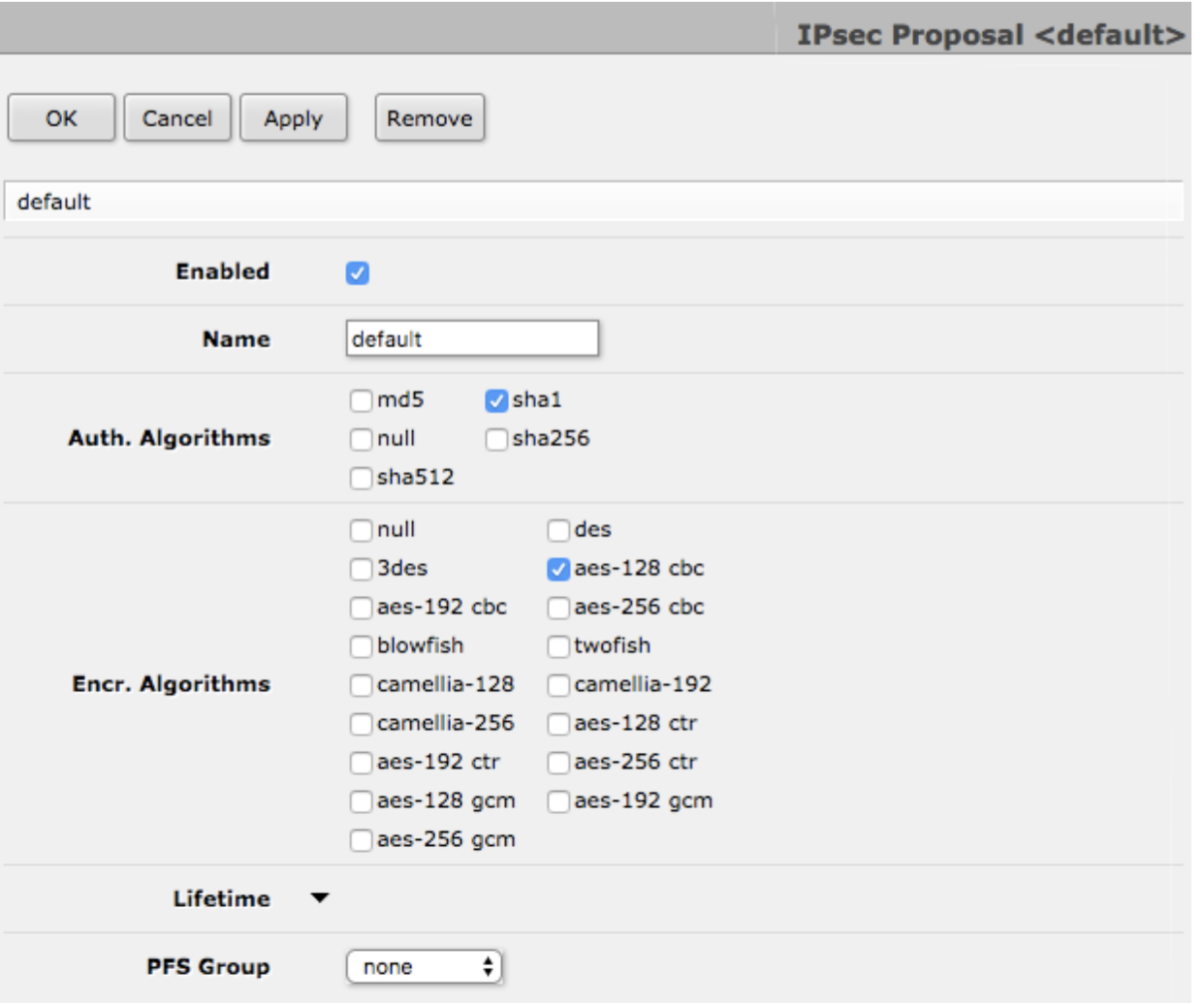
Configure encryption and authentication algorithms
IPSec Proposal Settings:
- ✓ Enabled
- Auth Algorithms: sha1 only
- Encr Algorithms: aes-128-cbc (or aes-256-cbc for higher security)
- PFS Group: none
3Create L2TP Interface
Navigate to: Interfaces → Add New → L2TP Client
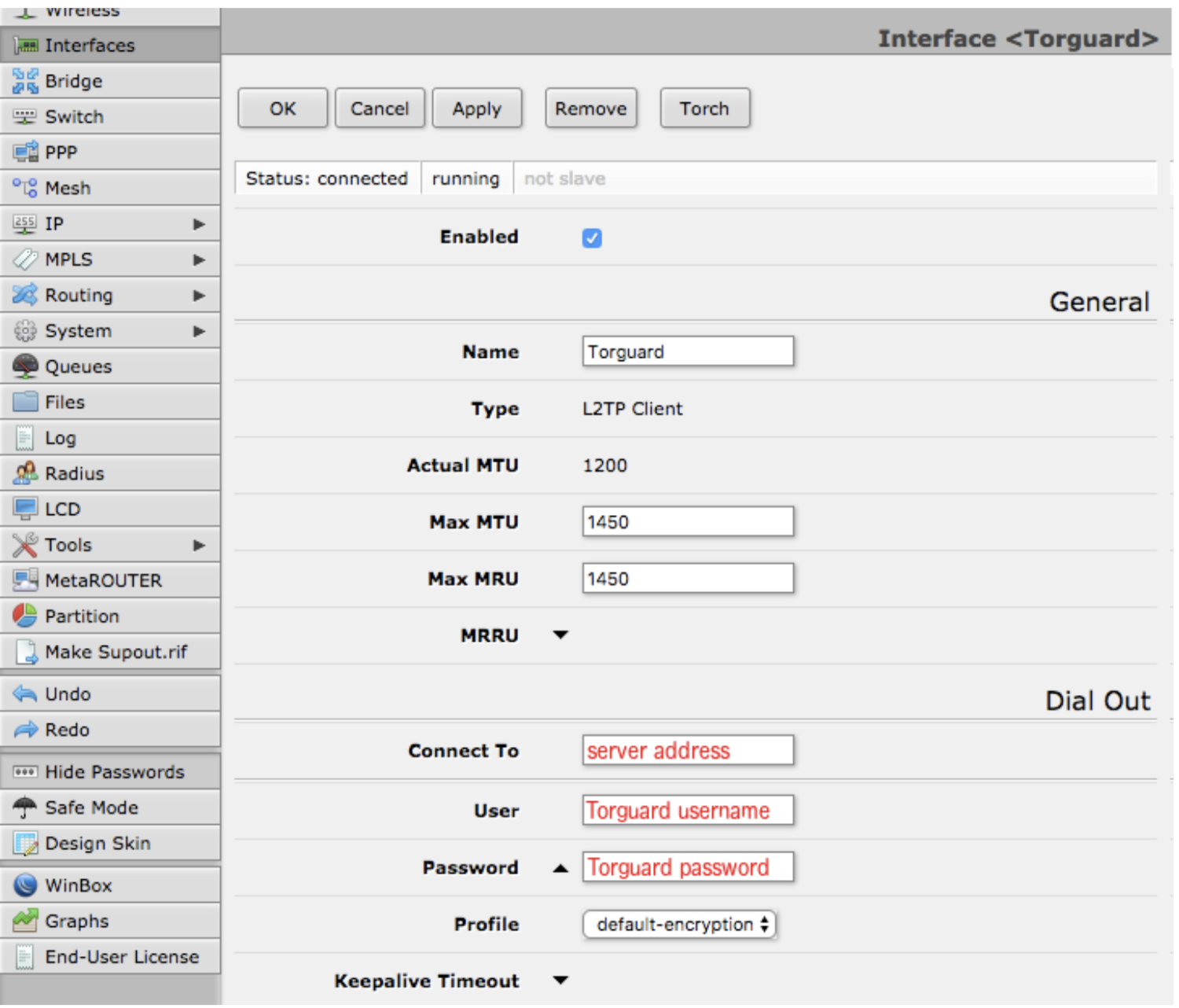
Basic L2TP client settings
General Settings:
- ✓ Enabled
- Name: TorGuard-L2TP
Dial Out Settings:
- Connect To: [VPN Server IP]
- User: Your TorGuard Username
- Password: Your TorGuard Password
- ✓ Use IPsec
- IPsec Secret: torguard
- ✗ Dial On Demand (unchecked)
- ✗ Add Default Route (unchecked)
4Disable Fasttrack (Important!)
Navigate to: IP → Firewall → Filter Rules
⚠️ Critical Step
Find any rules with "fasttrack connection" and disable them. Fasttrack bypasses connection tracking and will break VPN functionality.
5Configure NAT Masquerade
Navigate to: IP → Firewall → NAT → Add New
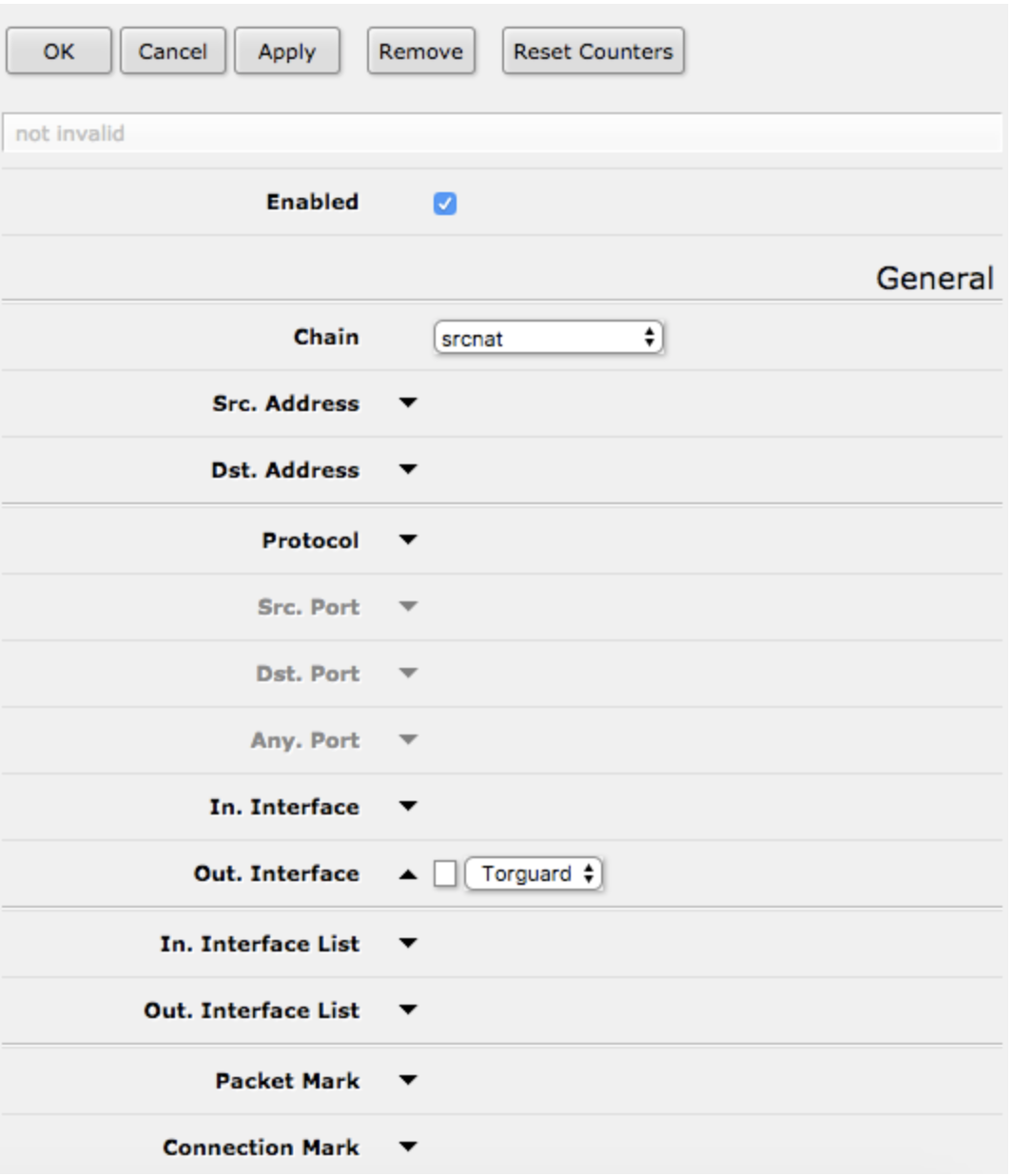
NAT Rule:
- Chain: srcnat
- Out Interface: TorGuard-L2TP
- Action: masquerade
6Setup Selective Routing (Optional)
For routing specific devices through VPN:
A. Create Mangle Rule
Navigate to: IP → Firewall → Mangle → Add New
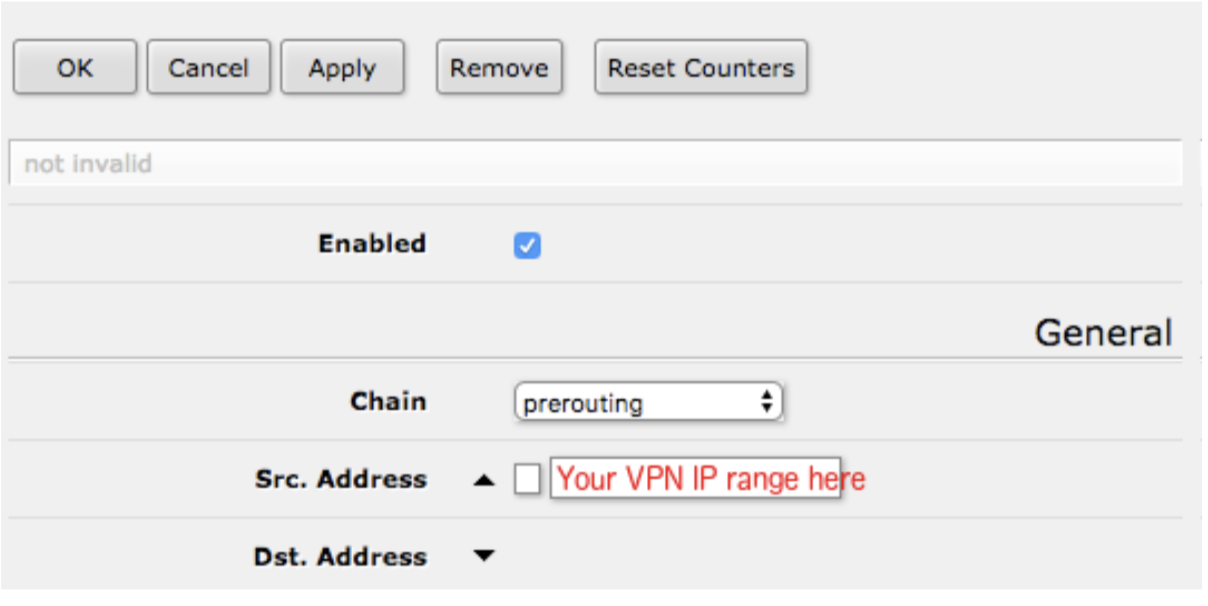
Mangle Settings:
- ✓ Enabled
- Chain: prerouting
- Src Address: 192.168.88.100-192.168.88.150 (example range)
- Action: mark routing
- New Routing Mark: VPN-Route
- ✓ Passthrough
B. Create Route
Navigate to: IP → Routes → Add New
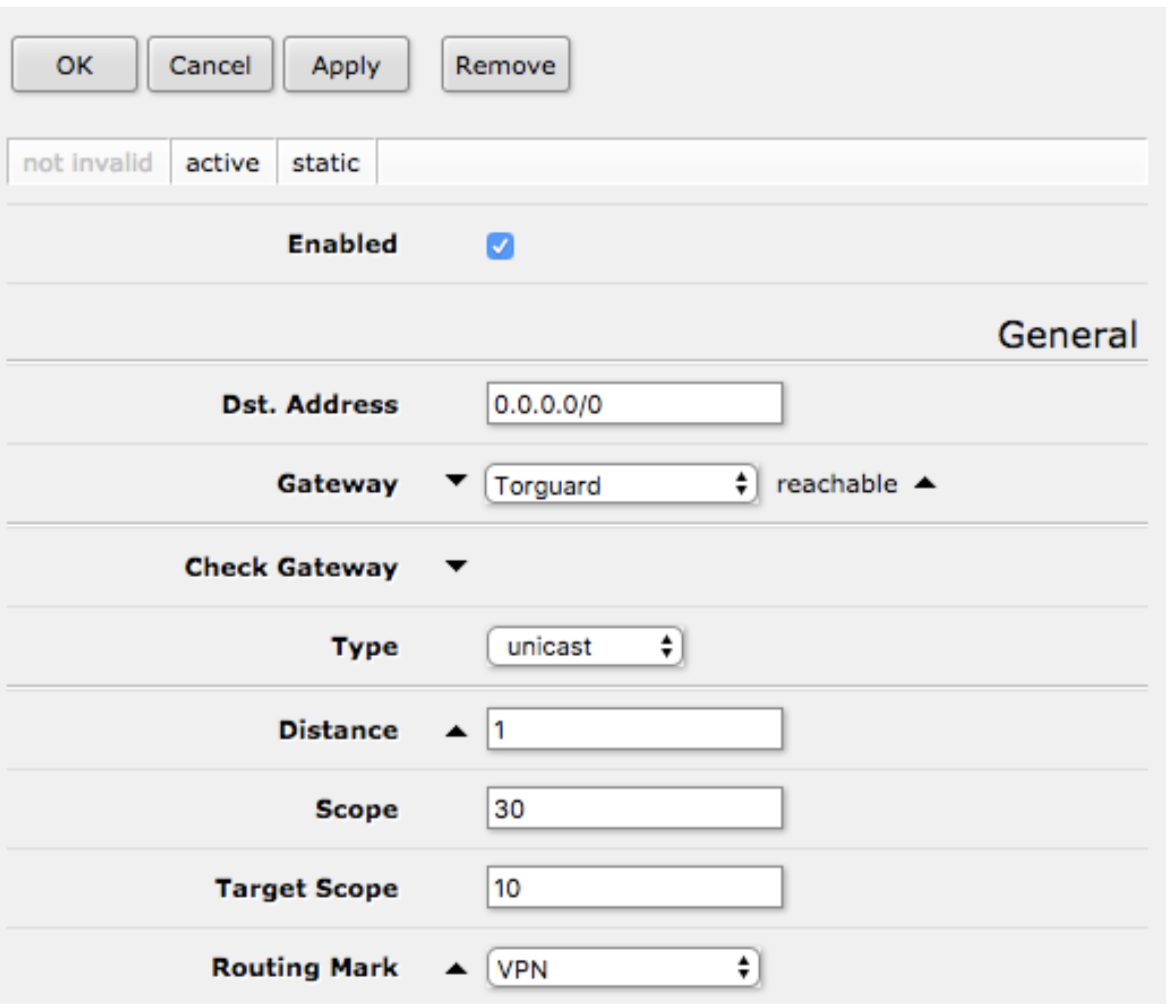
Route Settings:
- Dst Address: 0.0.0.0/0
- Gateway: TorGuard-L2TP
- Routing Mark: VPN-Route
7Configure DNS
Navigate to: IP → DNS
TorGuard DNS Servers:
- Primary: 10.8.0.1
- Secondary: 10.8.8.1
- ✓ Allow Remote Requests
Traffic Flow Visualization
Selective VPN Routing
(192.168.88.100)
(Mark: VPN-Route)
(Gateway: L2TP)
Performance Optimization
🚀 Optimization Tips
CPU Usage Reduction:
- Use AES-128 instead of AES-256 if security permits
- Enable hardware encryption if your RouterBoard supports it
- Limit concurrent connections
- Consider upgrading to RouterOS 7 for WireGuard
Connection Stability:
- Set keepalive timeout: 10 seconds
- Enable DPD (Dead Peer Detection)
- Use stable DNS servers
- Monitor MTU issues (typically 1400 for L2TP/IPSec)
Troubleshooting
Connection Fails
- Verify server IP is correct
- Check username/password
- Ensure ports 500, 4500 (UDP) open
- Disable fasttrack rules
No Internet Access
- Check NAT masquerade rule
- Verify DNS configuration
- Test with manual DNS (8.8.8.8)
- Check firewall filter rules
Poor Performance
- Monitor CPU usage (/system resource)
- Switch to AES-128
- Check for packet fragmentation
- Consider protocol alternatives
Command Line Configuration
For advanced users, here's the complete configuration via CLI:
# IPSec Proposal
/ip ipsec proposal
set [ find default=yes ] auth-algorithms=sha1 enc-algorithms=aes-128-cbc pfs-group=none
# L2TP Client
/interface l2tp-client
add connect-to=SERVER_IP disabled=no ipsec-secret=torguard name=TorGuard-L2TP \
password=YOUR_PASSWORD use-ipsec=yes user=YOUR_USERNAME
# NAT Rule
/ip firewall nat
add action=masquerade chain=srcnat out-interface=TorGuard-L2TP
# Mangle Rule (optional - for selective routing)
/ip firewall mangle
add action=mark-routing chain=prerouting new-routing-mark=VPN-Route \
passthrough=yes src-address=192.168.88.100-192.168.88.150
# Route (optional - for selective routing)
/ip route
add distance=1 gateway=TorGuard-L2TP routing-mark=VPN-Route
# DNS
/ip dns
set allow-remote-requests=yes servers=10.8.0.1,10.8.8.1
Security Best Practices
✅ Recommendations
- Firewall Rules: Create specific allow rules for VPN traffic only
- Logging: Enable connection logging for audit trails
- Updates: Keep RouterOS updated for security patches
- Backup: Export configuration before making changes
- Migration Plan: Consider upgrading to WireGuard or IKEv2
When to Use L2TP/IPSec
L2TP/IPSec is suitable when:
- WireGuard and IKEv2 are not available
- Compatibility with legacy systems is required
- PPTP needs to be replaced with something more secure
- Temporary solution while planning modern protocol deployment
Need Help?
If you need assistance with L2TP/IPSec configuration:
Include your RouterOS version and specific error messages