Prerequisites
Before setting up an SSH tunnel with Bitvise, ensure you have:
- Windows 7, 8, 10, or 11 operating system
- Active TorGuard account with SSH tunnel service
- Your TorGuard SSH server details and credentials
- Administrator access on your Windows computer
- Firefox, Chrome, or another SOCKS5-compatible browser
Benefits of SSH Tunneling
SSH tunnels provide several advantages over standard proxy connections:
- Military-Grade Encryption: All traffic is encrypted using SSH protocol
- Bypass Restrictions: Overcome firewalls and content filters
- Stealth Mode: Traffic appears as regular SSH connections
- Port Flexibility: Use multiple ports to avoid blocking
- Obfuscation Support: Hide SSH traffic from deep packet inspection
Step 1: Enable SSH Tunnel Service
- Log in to your TorGuard member area
- Navigate to SSH Tunnel Settings
- Enable SSH tunnel service for your desired location
- Note down the following information:
- SSH server IP address
- Available ports (typically 22, 443, or custom ports)
- Obfuscation key (if using obfuscation)
Step 2: Download and Install Bitvise
- Visit the official Bitvise website: Download Bitvise SSH Client
- Download the latest version for Windows
- Run the installer as Administrator
- Follow the installation wizard:
- Accept the license agreement
- Choose installation directory (default is fine)
- Select "Install for all users"
- Complete the installation
- Launch Bitvise SSH Client from the Start Menu
Step 3: Configure SSH Connection in Bitvise
In the Bitvise main window, configure the Login tab with your TorGuard SSH details:
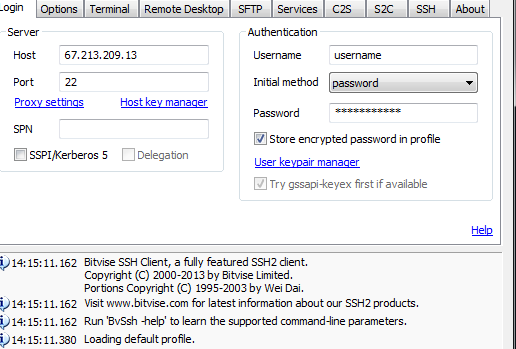
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Host | Your SSH server IP (from activation email) |
| Port | 22 (default) or custom port from server list |
| Username | Your TorGuard VPN/Proxy username |
| Initial method | password |
| Password | Your TorGuard VPN/Proxy password |
| Store encrypted password | Check this for convenience |
Optional: Configure Obfuscation
If you need to hide SSH traffic from deep packet inspection:
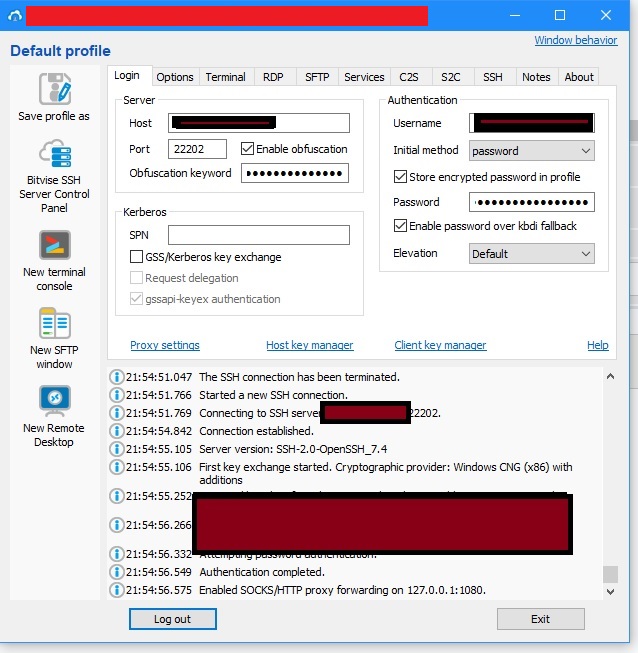
- Click the SSH tab in Bitvise
- Enable Obfuscation
- Enter the obfuscation keyword from your SSH settings page
- Use the corresponding obfuscated port (not port 22)
Step 4: Configure SOCKS5 Proxy Forwarding
Click the Services tab and configure proxy forwarding:
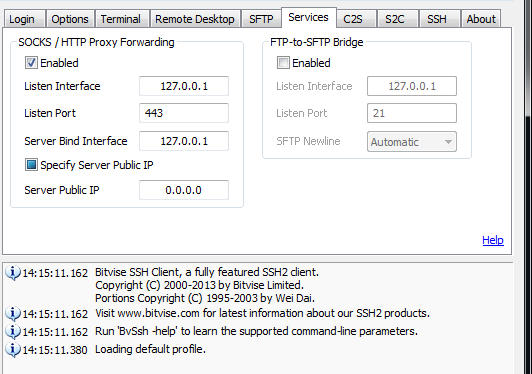
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| SOCKS/HTTP Proxy Forwarding | Enabled (check the box) |
| Listen interface | 127.0.0.1 |
| Listen port | 1080 (or any preferred port like 443) |
| Server bind interface | 127.0.0.1 |
| Server bind port | 0.0.0.0 |
Step 5: Establish SSH Connection
- Review all settings to ensure accuracy
- Click the Login button in Bitvise
- If this is your first connection, you'll see a host key verification dialog:
- Click Accept and Save to store the server's key
- This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
- Wait for the connection to establish
- You should see "Authentication completed" in the log window
- The Bitvise window will minimize to the system tray
Step 6: Configure Your Browser
Firefox Configuration
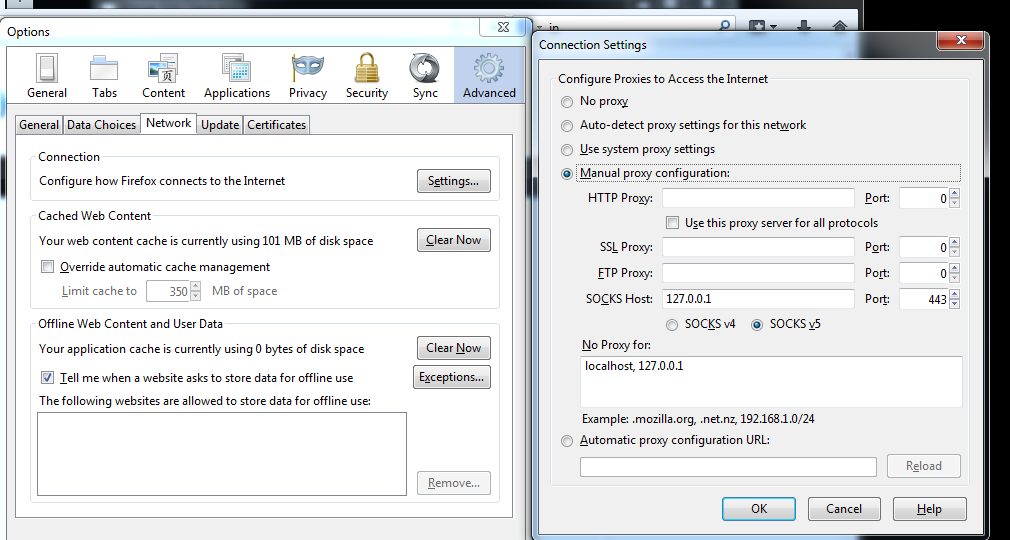
- Open Firefox and go to Settings (☰ menu → Settings)
- Scroll down to Network Settings
- Click Settings... button
- Configure as follows:
- Select Manual proxy configuration
- SOCKS Host: 127.0.0.1
- Port: 1080 (or your chosen port)
- Select SOCKS v5
- Check Proxy DNS when using SOCKS v5
- Click OK
Chrome Configuration
For Chrome, you'll need to use a proxy extension or command-line flags:
Option 1: Using Proxy Extension
- Install Proxy SwitchyOmega
- Create new profile → Select "Proxy Profile"
- Protocol: SOCKS5
- Server: 127.0.0.1
- Port: 1080
- Apply changes and enable the profile
Option 2: Command Line
chrome.exe --proxy-server="socks5://127.0.0.1:1080"
Verifying Your Connection
After configuring your browser, verify the SSH tunnel is working:
- Visit TorGuard IP Check
- Confirm your IP shows the SSH server location
- Check for DNS leaks at DNS Leak Test
- Test browsing speed and functionality
Advanced Configuration
Multiple Port Forwarding
You can forward multiple ports through the SSH tunnel:
- In Bitvise Services tab, click Add
- Configure additional SOCKS or port forwards
- Use different local ports for different services
Auto-Reconnection
Enable automatic reconnection for persistent tunnels:
- In Bitvise, go to Options tab
- Enable Reconnect automatically
- Set reconnection delay (5-10 seconds recommended)
System-Wide Proxy
To route all Windows traffic through the tunnel:
- Windows Settings → Network & Internet → Proxy
- Manual proxy setup → Use a proxy server
- Address: 127.0.0.1, Port: 1080
- Note: Not all Windows apps respect system proxy settings
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Fails
- Check credentials: Ensure using VPN/Proxy username, not website login
- Verify server IP: Confirm SSH server is active in member area
- Try different port: Some networks block port 22, try 443 or 80
- Windows Firewall: Add Bitvise to firewall exceptions
Slow Connection Speed
- Server location: Choose geographically closer servers
- Compression: Enable compression in Bitvise SSH settings
- Encryption: Try different cipher algorithms (AES-128 is faster)
- Network congestion: Test at different times of day
Browser Not Using Proxy
- Check proxy settings: Ensure correct SOCKS5 configuration
- Browser cache: Clear cache and cookies
- Extensions conflict: Disable VPN/proxy extensions
- DNS over HTTPS: Disable in browser settings
Security Best Practices
- Use strong passwords: Enable two-factor authentication if available
- Keep Bitvise updated: Install security updates promptly
- Verify host keys: Don't ignore host key warnings
- Use obfuscation: In restrictive networks or countries
- Monitor connections: Check Bitvise activity log regularly
Alternative SSH Clients
While Bitvise is recommended, alternatives include:
- PuTTY: Free, lightweight, but less user-friendly
- MobaXterm: Feature-rich with X11 forwarding
- SecureCRT: Professional tool with advanced features
- OpenSSH: Built into Windows 10/11 (command-line)
Comparing SSH to Other Protocols
| Feature | SSH Tunnel | VPN | SOCKS5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Strong | Strong | None |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate | Fastest |
| Compatibility | App-specific | System-wide | App-specific |
| Stealth | High | Low | Moderate |